As smartphones enter the AI-native era, chip technology is iterating at an unprecedented rate. According to the latest forecast of market research firm Counterpoint Research, by 2026, smartphone system-on-chip (SoC) shipments based on 2nm and 3nm processes will account for one-third of the overall market. This trend not only reflects the logical inevitability of technological evolution, but also is a concentrated embodiment of the joint promotion of market demand upgrading and industrial chain reconstruction.
First, the advanced process is advancing rapidly, and 2nm mass production is just around the corner
The evolution of the chip manufacturing process has been a key driver of the leap in smartphone performance. From 5nm, 4nm to 3nm, and then to 2nm, which is about to be mass-produced, behind every node leap is a collaborative breakthrough in transistor structure, process optimization and production line capabilities.
Taking TSMC as an example, its 3nm process N3 will be commercialized for the first time in 2023 on the A17 Pro chip of Apple's iPhone 15 Pro series, achieving significant performance and energy efficiency improvements. According to data released by Apple, the A17 Pro's built-in neural network engine can perform 33 trillion operations per second (TOPS), and the GPU performance is improved by 2x compared to the previous generation, and the overall power consumption is reduced by about 20%.
TSMC has announced that it will enter the trial production stage of the 2nm process (N2) in the second half of 2025 and officially mass production in 2026. The N2 process uses a GAA (Surround Gate) transistor architecture, which has stronger electronic control capabilities than the FinFET architecture, and can integrate more logic cells in the same area, which is expected to bring about 25% to 30% reduction in power consumption and 10% to 15% performance improvement.
Samsung, despite the yield challenges of its first-generation 3nm GAA in mass production in 2023, has gradually improved its capacity bottlenecks through subsequent OEM customer adjustments and process optimization, and plans to achieve commercial mass production of 2nm in 2026. Intel is not far behind, and its 20A and 18A processes are also locked in the market between 2024 and 2025, and may become a potential choice for mobile phone SoC manufacturers in the future.
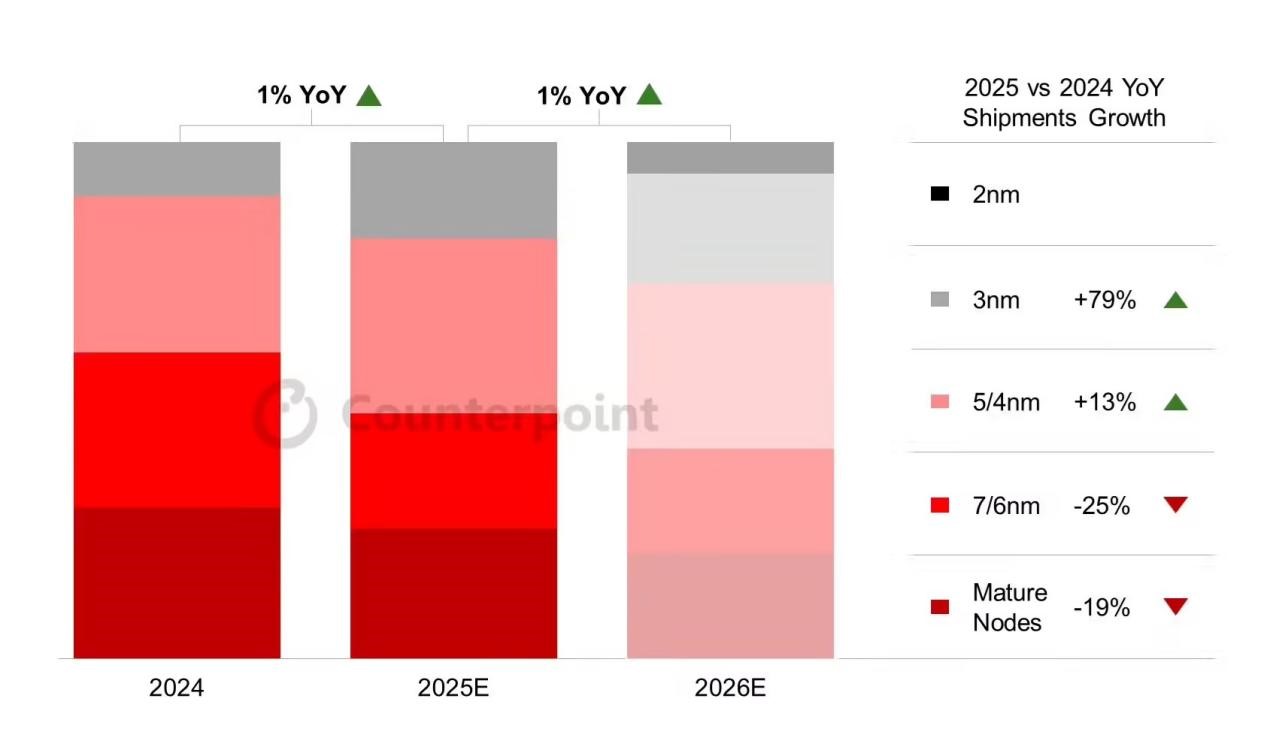
Image: CounterPoint estimates that 3nm/2nm mobile phone chips will account for one-third in 2026
Second, the demand for AI drives the explosive growth of high-performance chips
Behind the rapid evolution of mobile phone chips is the continuous improvement of AI capabilities on the device side. From speech recognition and image processing to the local operation of generative AI models, AI applications have gradually become the "standard" of flagship mobile phone chips.
Qualcomm and MediaTek will launch flagship SoCs based on 3nm processes in 2024, the Snapdragon 8 Gen3 and Dimensity 9300, respectively, which have achieved significant improvements in AI inference performance, multi-modal fusion capabilities, and graphics rendering. In 2025, the two companies are expected to continue to optimize their 3nm platform and introduce the 2nm process for the first time in the next generation of flagship chips to meet the comprehensive requirements of AI models for computing power, bandwidth, and energy efficiency ratio.
Market research firm IDC predicts that the AI smartphone chip market will reach $58 billion by 2026, an increase of nearly 70% from 2023. This growth is not only reflected in the high-end market, but is also penetrating into the mid-to-high-end product line, which means that advanced process chips will continue to expand their share of overall shipments.
Third, OEM pattern: TSMC's dominant position is stable, and Samsung is trying to break the situation
At present, in the advanced process foundry market of 5nm and below, TSMC occupies an absolute dominance with its technology maturity, yield and customer trust. In 2025, it is expected to account for 87% of mobile phone SoC foundry shipments at this node, and will increase to 89% in 2028.
Apple, Qualcomm, MediaTek and other leading fabless design companies are currently highly dependent on TSMC, especially in the field of high-performance mobile SoCs, which are almost irreplaceable. However, Samsung is also gradually regaining market share, through close cooperation with Google, AMD, and certain Chinese IC design companies, and focusing on 3nm and 2nm GAA processes, hoping to seize more foundry orders in 2026, forming a "duopoly" pattern with TSMC.
In addition, Intel's Foundry Business (IFS) is also actively seeking to enter the mobile SoC space, through the IDM 2.0 strategy and external collaboration, or will provide additional options after 2nm to enhance industry diversification.
Fourth, the dual challenges of rising costs and market differentiation are highlighted
Despite the performance dividends brought by advanced processes, their cost pressures cannot be ignored. According to Tianfeng International analyst Ming-Chi Kuo, the BOM cost of the Qualcomm Snapdragon 8 Gen3 Extreme Edition reaches $180, an increase of 15% compared with the Gen3 and accounts for more than 25% of the price of high-end smartphones. The unit wafer cost of chips using the 2nm process is expected to increase by another 15%-20%.
Not only that, memory chip prices will rise significantly in the first half of 2024, with DRAM contract prices rising by 13%-18% month-on-month, and NAND Flash prices rising by 15%-20%, further pushing up the cost of the whole machine.
Large manufacturers such as Apple, Samsung, Xiaomi, Honor, etc., with their strong supply chain bargaining power and product premium space, can still absorb the impact of rising costs and continue to promote the high-end market strategy. Small and medium-sized brands are facing huge survival pressure and lack competitiveness in the high-end market, so they are bound to shift the focus of resources to the low-end market, and make a living in the red sea through "cost-effective" and differentiated design.
This will lead to further differentiation of the mobile phone market structure in 2026: the high-end market will be concentrated in a few leading brands, while the low-end market will show a pattern of fierce competition and price involution.
Fifth, The technical threshold and sustainable pressure behind the advanced manufacturing process
As the process continues to move towards 2nm and beyond, the difficulty of manufacturing increases exponentially. The physical size of transistors is approaching the limit, and the complexity and cost of EUV lithography processes are exploding, and yield control has become the key to process success.
At the same time, the increase in power density brought about by advanced manufacturing processes also puts forward higher requirements for packaging technology and thermal design. How to maintain the battery life and thermal control ability of the mobile phone while ensuring the performance of the SoC will become a key issue for downstream manufacturers in the industrial chain.
In the dimension of environmental protection, the consumption of energy and water resources by advanced process nodes has increased dramatically. According to ASML and TSMC, EUV equipment consumes up to 1 megawatt of electricity per hour, and the annual fluorinated gas and cooling resources used by a single extreme ultraviolet lithography machine are much higher than those of traditional DUV processes. This puts forward higher requirements for green manufacturing for the entire industry, and ESG (environmental, social and governance) assessment indicators will become an important part of the global market competition between wafer foundries and brand factories.
Conclusion: The new cycle of smart chips has arrived, and enterprises and policies need to be driven by two wheels
Overall, in 2026, the smartphone chip market will usher in a new cycle with the 2nm/3nm process as the core, which is not only the embodiment of technological upgrading, but also will reshape the entire industrial pattern. Technological breakthroughs, AI demand, and foundry evolution are superimposed on each other, accelerating the high-level evolution of global mobile phone SoC competition.
However, behind the performance dividends, cost pressures, increased market concentration, environmental challenges and technical bottlenecks also constitute realistic problems that enterprises must face.
Relevant enterprises should strengthen the layout of advanced manufacturing processes, promote the technical collaboration of the whole chain of design, manufacturing and packaging, and improve the comprehensive capabilities of AI and green manufacturing, so as to take the initiative in the fierce competition in the future. In addition, policy support is also indispensable, and it is necessary to further promote the independence and controllability in core areas such as materials, equipment, and EDA tools, accelerate the construction of industrial ecology, and ensure the steady development of the chip strategic industry.






