With the rapid development of quantum computing technology, more and more technology companies and research institutions have begun to pay attention to its commercial application and potential. From Google's Sycamore processors to China's Zu Chongzhi 3.0 to IBM's hybrid quantum computing strategy, quantum computing is moving towards real-world applications. Although quantum computing is still far from being fully commercialized, its enormous potential has attracted global attention.
The concept of quantum computing can be traced back to 1981, when physicist Richard Feynman came up with a bold idea: to use the principles of quantum mechanics to perform calculations. This concept has laid a theoretical foundation for the development of quantum computing and opened a new journey for mankind to explore the mysteries of the quantum world.
In the decades that followed, quantum computing gradually moved from theoretical research to experimental exploration and practical application. Today, quantum computing is making remarkable progress, but it also faces many challenges. The basic principle of quantum computing is the use of qubits and the principle of superposition, which can be in a superposition state of 0 and 1 at the same time, unlike the binary bits used by traditional computers. This means that quantum computers are able to perform calculations in multiple states at the same time, which greatly increases computing power, especially when dealing with complex problems, much faster than classical computers.
Technological breakthroughs and innovations
Google and Quantum Error Correction
In the development of quantum computing, the error rate has been a key factor limiting its performance. Google's Willow processor features quantum error correction technology, which can significantly reduce the error rate and is a major breakthrough in the field of quantum computing. Through quantum error correction, the reliability and stability of quantum computers have been greatly improved, laying the foundation for more complex quantum computing tasks.
IBM's hybrid approach to quantum computing
IBM has proposed a "hybrid computing" approach that combines quantum computing and classical computing. This approach utilizes quantum computing to speed up specific tasks, while classical computers are used to deal with more general problems. In addition, IBM is working on "circuit cutting" techniques to overcome the problem of limited qubits in quantum computing. Larger-scale quantum computing is achieved by decomposing complex quantum circuits into smaller subcircuits, executing them on different quantum devices, and then integrating the results.
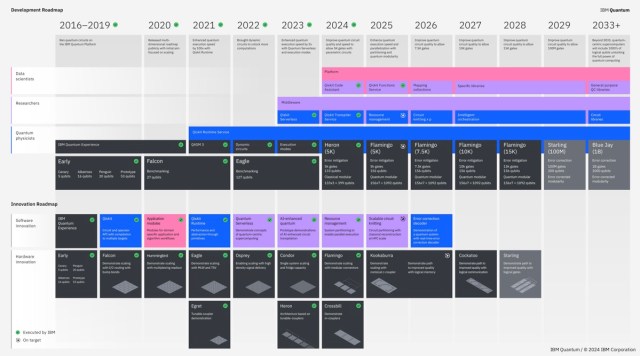
Figure:IBM Quantum Roadmap (source:IBM Press)
In addition, with Zu Chongzhi's series of superconducting quantum computers, China has become a major contender in the quantum race, questioning Google's claims of hegemony. The latest version of Zu Chongzhi 3.0 has 105 qubits and has extraordinary fidelity.
Zu Chongzhi 3.0 also used an 83-qubit, 32-period random circuit sampling experiment to produce 1 million samples in a few seconds. With this achievement, Zu Chongzhi 3.0 has realized the advantages of quantum computing together with Google's Willow.
The need for global cooperation
The realization of quantum computing requires global cooperation. No single country or company can accomplish this complex task alone. Scientific research teams in different countries and regions have their own advantages in different fields of quantum computing, and the development of quantum computing technology can be accelerated by strengthening international cooperation and resource sharing. For example, international research collaborations can bring together the world's top scientists and engineers to tackle key technical challenges in quantum computing.
Potential applications of quantum computing
The potential applications of quantum computing are broad and far-reaching, spanning fields such as medicine, drug discovery, materials science, cybersecurity, and artificial intelligence. In the medical field, quantum computing can accelerate the drug discovery process, by simulating complex biomolecular structures and chemical reactions, to quickly screen for effective drug candidates. In materials science, quantum computing helps discover and design novel materials that may have unimaginable properties, such as higher strength, better electrical conductivity, and lower weight. In terms of cybersecurity, quantum computing's superior computing power can crack existing encryption algorithms, while also prompting researchers to develop more secure quantum encryption technologies. In the field of artificial intelligence, quantum computing can process massive amounts of data and train more complex and accurate machine learning models, driving the rapid development of artificial intelligence technology.






